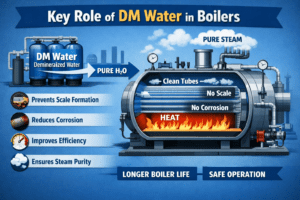
Boilers are critical equipment in many industries, including power generation, pharmaceuticals, food processing, textiles, and chemicals. The efficiency, safety, and lifespan of a boiler largely depend on the quality of water used. Demineralized (DM) water plays a vital role in ensuring smooth boiler operation by eliminating impurities that can cause scaling, corrosion, and system failures.
What is Demineralised Water?
Demineralized water is water from which dissolved minerals and salts-such as calcium, magnesium, sodium, chlorides, sulfates, and silica-have been removed through processes like ion exchange, reverse osmosis, or electro deionization. The result is high purity water with very low conductivity and total dissolved solids (TDS).
Why Water Quality Matters in Boilers?
Boilers operate at high temperatures and pressures. Any dissolved minerals or contaminants in feed water can concentrate during steam generation, leading to operational and safety issues. Using untreated or partially treated water can significantly reduce boiler efficiency and increase maintenance costs.
Key Roles of DM Water in Boiler Systems
- Prevents Scale Formation
Minerals such as calcium and magnesium form hard scale deposits on boiler tubes and heat transfer surfaces. Scale acts as an insulator, reducing heat transfer efficiency and increasing fuel consumption. DM water, being free from these minerals, prevents scale buildup and ensures efficient heat transfer.
- Reduces Corrosion
Dissolved salts, oxygen, and chlorides in water can cause corrosion of boiler components, leading to tube failure and leaks. DM water minimizes ionic content, thereby reducing electrochemical reactions that cause corrosion and extending the life of the boiler system.
- Improves Heat Transfer Efficiency
Clean, mineral-free water allows uniform heat transfer across boiler surfaces. This results in faster steam generation, stable operation, and lower energy losses, contributing to overall process efficiency.
- Enhances Boiler Safety
Scale and corrosion can cause localized overheating, which may lead to tube rupture or boiler explosion in extreme cases. By using DM water, these risks are minimized, ensuring safer boiler operation.
- Reduces Blowdown Losses
High mineral content in boiler water requires frequent blowdown to control TDS levels. Since DM water has very low dissolved solids, blowdown frequency is reduced, leading to savings in water, energy, and treatment chemicals.
- Extends Equipment Life
Consistent use of DM water protects boiler internals, valves, pipelines, and turbines from deposits and corrosion. This extends equipment lifespan and reduces unplanned shutdowns and maintenance expenses.
- Supports High-Pressure Boilers
High-pressure and supercritical boilers demand extremely pure feed water. Even trace impurities can cause serious damage. DM water meets the stringent quality requirements essential for such advanced boiler systems.
Typical DM Water Quality Requirements for Boilers
- Very low conductivity
- Low silica content
- Negligible hardness
- Low sodium and chloride levels (Exact specifications depend on boiler pressure and design.)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1 What is DM water and why is it used in boilers?
Demineralised (DM) water is water with dissolved salts and minerals removed. It is used in boilers to prevent scaling, corrosion, and deposits that can reduce efficiency and damage equipment.
Q2 How does DM water prevent scale formation in boilers?
DM water contains negligible calcium and magnesium, which are the main causes of scale. This keeps boiler tubes and heat transfer surfaces clean.
Q3 How does DM water reduce boiler corrosion?
By removing ions such as chlorides and sulphates that cause electrochemical reactions,
DM water minimizes corrosion and extends boiler life.
Q4 Why is low conductivity important in boiler feed water?
Low conductivity indicates minimal dissolved salts. This helps maintain steam purity, reduces blowdown frequency, and prevents internal boiler damage.
Q5 Why is DM water essential for high-pressure boilers?
High pressure boilers require extremely pure water. Even trace impurities can cause scaling and turbine damage, making DM water essential.
Q6. How does DM water affect boiler safety?
DM water prevents scale and corrosion that can cause tube overheating, leaks, and boiler failures, improving operational safety.
CONCLUSION
Demineralised water is not just a preference but a necessity for modern boiler systems. By preventing scale and corrosion, improving heat transfer, enhancing safety, and reducing operational costs, DM water plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient and reliable boiler performance. Industries that invest in high-quality DM water systems benefit from improved efficiency, longer equipment life, and lower total operating costs.